Reversing a linked list means re-arranging the next (connection) pointers. Head will point to the last node and the first node will point to NULL. Direction of other next pointers will change.
If a linked list looks like this:

After reversal, it will look like:

Logic to Reverse a Linked List
- Take the first node out of the linked list. One new pointer will point to the first node and the head will move to the next node.
- Insert the node at the from of the new list.
- Repeat previous two steps until all nodes move to the new list.
- Pointer the head of the original linked list to the first node of the new list.
Reverse Linked List Program
/*
* File name: test.c
* Compile: cc test.c
* */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int val;
struct node *next;
};
void print_list(struct node *head)
{
printf("H->");
while(head)
{
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("|||\n\n");
}
void insert_front(struct node **head, int value)
{
struct node * new_node = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to insert element. Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
void reverse_linked_list(struct node **head) {
struct node *new_head = NULL; /*head of the reversed list*/
struct node *tmp = NULL;
while(*head) {
tmp = *head; /*tmp points the first node of the current list*/
*head = (*head)->next;
/*Insert tmp at the front of the reversed list.*/
tmp->next = new_head;
new_head = tmp;
}
*head = new_head;
}
void main()
{
int count = 0, i, val;
struct node * head = NULL;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("Enter %dth element: ", i);
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_front(&head, val);
}
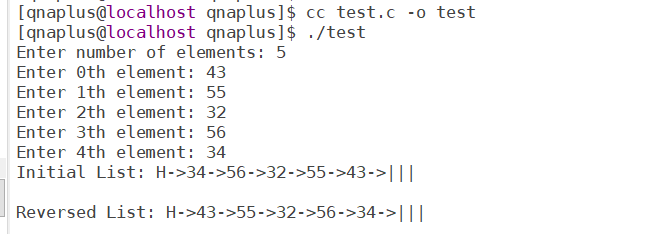
printf("Initial List: ");
print_list(head);
reverse_linked_list(&head);
printf("Reversed List: ");
print_list(head);
}
This program first takes input of integers and put them into a linked list using insert_front() function. Then the reverse_linked_list() is called to reverse the list.
Here is the output of the program.
Using Three Pointers
Instead of constructing a new list, we can reverse a linked list with the help of three pointers.
Logic to Reverse a Linked List Using There Pointer.
- Initialize three pointers, prev to NULL, cur to head and next to head->next.
- Until cur becomes NULL, assign next to next->next, cur->next to prev, prev to cur and cur to next.
- At the end point head to prev.
Here is the modified reverse_linked_list() function.
void reverse_linked_list(struct node **head) {
struct node *prev = NULL;
struct node *cur = NULL;
struct node *next = NULL;
cur = *head;
if(*head) next = (*head)->next;
while(cur) {
next = next->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
*head = prev;
}Read also: Sort a Linked List.