Here we’ll see how to write C Program to move the last node to the front of a linked list. We can do that just by re-arranging the pointers. No need to create or delete any node.
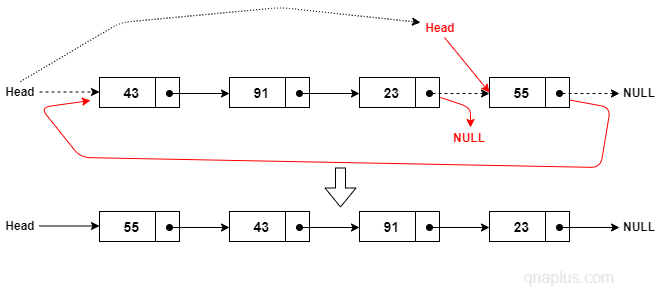
Logic to Move the Last Node to the Front
- If the linked list is empty or has only one element, then return. If the list has only one element, then the first node and the last node are basically same.
- Point prev to the first node and cur to the second node.
- Keep moving both prev and cur to the next nodes until cur->next becomes NULL. cur->next pointing to NULL means cur pointing to the last node and prev pointing to the second last node.
- Point the second last node to NULL (prev->next = NULL), last node to the first node (cur->next = head). And assign head where cur is pointing to (head = cur).
The Program
/*File: test.c*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int val;
struct node *next;
};
/*Move the last node to the front.*/
void move_last_node_to_front(struct node **head) {
struct node *prev = NULL, *cur = NULL;
/*Return if there is no node or only one node*/
if(head == NULL || *head == NULL || (*head)->next == NULL) return;
prev = *head;
cur = prev->next;
/*Going to the last node*/
while(cur->next) {
prev = prev->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
cur->next = *head;
*head = cur;
}
/*Print the linked list*/
void print_list(struct node *head) {
printf("H->");
while(head)
{
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("|||\n");
}
/*Insert an element at the front of the list*/
void insert_front(struct node **head, int value) {
struct node * new_node = NULL;
/*Allocating memory for the new node*/
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to insert element. Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
/*Pointing the new node to where head is currently pointing to*/
new_node->next = *head;
/*Pointing head to new node.*/
*head = new_node;
}
void main()
{
int count = 0, i, val;
struct node * head = NULL;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("Enter %dth element: ", i);
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_front(&head, val);
}
printf("Initial Linked List: ");
print_list(head);
move_last_node_to_front(&head);
printf("Linked List after movinf last node to front: ");
print_list(head);
}
This program first takes input of some numbers to create the linked list. Then it calls the move_last_node_to_front() function to move the last node to the front.
Here is the output.
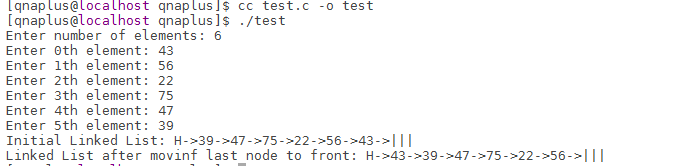
From the output we can see that initially 43 was the last node. After the move_last_node_to_front() function call, it became the first node of the linked list.
Read also: Insert an element to a linked list.